by Jason Wasserman MD PhD FRCPC
January 17, 2024
A hyperplastic polyp is a non-cancerous growth typically found in the descending (left) colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum. It is a very common type of colorectal polyp. The polyp is made up of glandular cells normally found on the inside surface of the colon and rectum.
Can a hyperplastic polyp turn into cancer?
No. Hyperplastic polyps in the colon and rectum are benign (non-cancerous) growths that will not turn into cancer over time.
How is this diagnosis made?
The diagnosis of a hyperplastic polyp is usually made after the polyp is removed during a medical procedure called a colonoscopy. The polyp may be removed in one piece or multiple pieces. The tissue sample is then sent to a pathologist for examination.
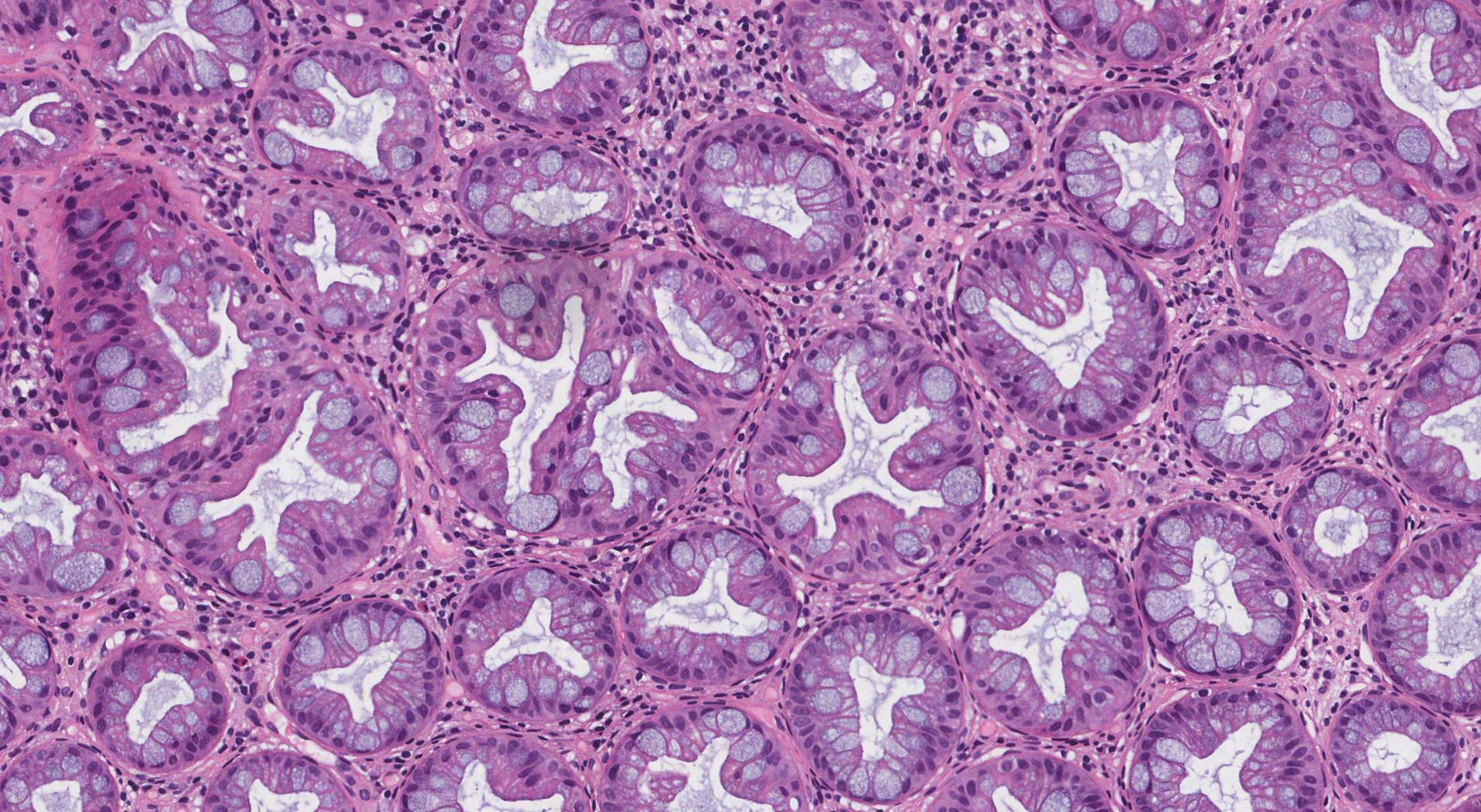
Microscopic features
When examined under the microscope, a hyperplastic polyp is made up of glands that are larger and have more epithelial cells than normal glands in the colon. When viewed on their short axis, some of the glands appear to be star-shaped.
Can a hyperplastic polyp grow back after being removed?
Hyperplastic polyps do not grow back once they are removed completely. However, it is very common for new hyperplastic polyps to develop. Although hyperplastic polyps usually pose no risk to your health, they can look very similar to other kinds of colonic polyps, some of which are associated with cancer. For that reason, all polyps, including hyperplastic polyps, should be removed and sent to a pathologist for examination under the microscope.
About this article
This article was written by medical doctors in conjunction with patient advisers. It was designed to help patients read and understand their pathology report. If you have any questions about this article, please contact us.



