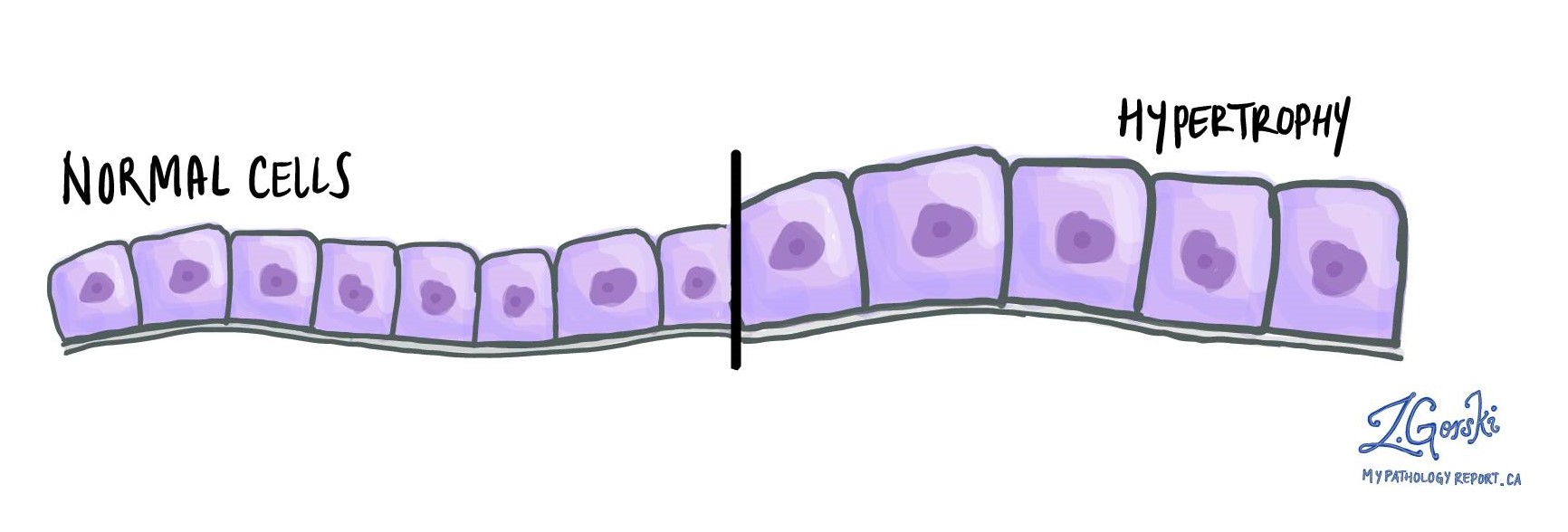
Hypertrophy is a non-cancerous condition characterized by an increase in the size of individual cells, resulting in an overall enlargement of the affected tissue or organ. It differs from hyperplasia, which involves increasing the number of cells rather than their size. The term hypertrophic is also used to describe tissues that have undergone hypertrophy.
What causes hypertrophy?
Common reasons why tissues or organs undergo hypertrophy include:
-
Increased physical demand: Tissues such as muscles grow larger when regularly exposed to physical activity or exercise.
-
Hormonal stimulation: Hormones can trigger cell enlargement, such as uterine muscle growth during pregnancy.
-
Long-term stress or disease: Chronic conditions, like high blood pressure, can cause the heart muscle to enlarge as it works harder.
Types of hypertrophy
Hypertrophy is categorized based on its underlying cause and effects:
-
Physiological hypertrophy: Beneficial or adaptive enlargement that improves the function of an organ or tissue. For example, muscle growth occurs from regular exercise.
-
Pathologic hypertrophy: Enlargement due to disease, injury, or long-term stress that typically impairs organ function, such as heart muscle enlargement from chronic high blood pressure.
Examples of hypertrophy
-
Muscles: Regular exercise causes skeletal muscles to enlarge, making them stronger and better able to handle increased physical activity.
-
Uterus: During pregnancy, hormonal changes cause the uterine muscles to enlarge, allowing the uterus to accommodate a growing baby.
-
Heart: The heart muscle may enlarge from regular exercise (physiologic hypertrophy) or conditions like chronic high blood pressure or heart valve problems (pathologic hypertrophy). While exercise-induced hypertrophy typically benefits heart health, disease-related hypertrophy can impair heart function.
How is hypertrophy identified?
Pathologists or physicians identify hypertrophy by examining tissue samples under a microscope or through imaging studies, such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans. They compare the size of the cells or tissues to normal, healthy tissue to determine if hypertrophy is present.
Is hypertrophy dangerous?
The significance of hypertrophy depends on its cause and location:
-
Physiological hypertrophy: Generally beneficial and improves tissue or organ function.
-
Pathologic hypertrophy: Can lead to serious health complications, such as heart failure when involving the heart muscle.
Your doctor must determine the cause of hypertrophy to recommend the appropriate treatment or lifestyle adjustments.
Hypertrophy versus hyperplasia
-
Hypertrophy means cells grow larger, but the cell count remains unchanged.
-
Hyperplasia means the number of cells increases, but individual cells stay the same size.
Both conditions result in tissue growth, but they differ in their mechanisms and implications.
Questions to ask your doctor
-
Which of my tissues or organs shows hypertrophy?
-
Is the hypertrophy physiologic (normal and healthy) or pathologic (related to a health condition)?
-
What caused the hypertrophy, and is treatment necessary?
-
Could this hypertrophy lead to complications or health risks?
-
Do I need any additional tests or ongoing monitoring?