MyPathologyReport
December 12, 2023
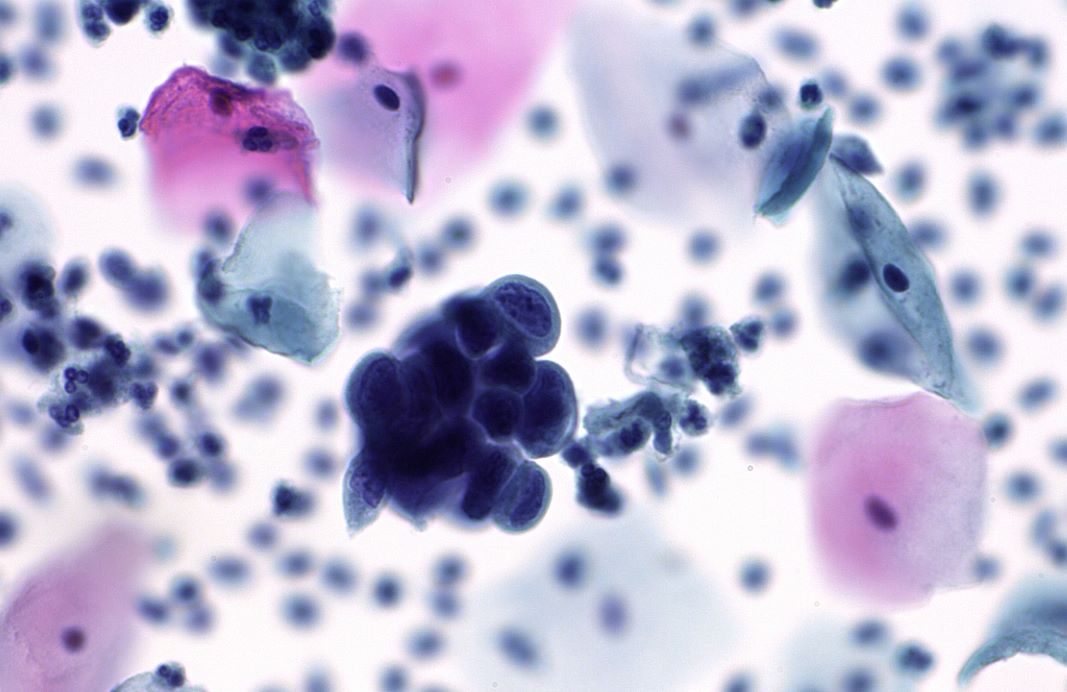
A Pap test, also known as a Pap smear, is a screening procedure used to detect precancerous and cancerous conditions in the cervix and anal canal. The test involves collecting a sample of cells from the cervix or anal canal. The cells are then examined under a microscope by a pathologist with the results provided in a pathology report.
Why is a Pap test performed?
The Pap test is primarily designed to detect changes in cervical or anal canal cells caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, which is a major risk factor for both cervical and anal cancer. If precancerous or cancerous cells are identified additional tests or procedures will usually be recommended.
Who should get a Pap test?
The Pap test is a vital tool for early detection and prevention of cervical cancer, and routine screenings are typically recommended for women, starting at around the age of 21. The frequency of Pap tests may vary based on age and individual health history. Anal Pap tests are recommended for both men and women over the age of 25 who have a history of HPV infection, have HIV, or are immunosuppressed for another reason.
How is a Pap test of the cervix performed?
Here is an overview of the procedure used to perform a Pap test of the cervix:
- Preparation: The Pap test is a relatively simple and quick procedure often performed during a pelvic examination. To ensure accurate results, it’s recommended to avoid using tampons, vaginal medications, or douches for at least 48 hours before the test. Additionally, it’s best to schedule the test when you are not menstruating.
- Positioning: You will typically lie on your back on an examination table with your feet placed in stirrups to allow the doctor access to the pelvic area.
- Speculum insertion: The doctor will gently insert a speculum into the vagina to widen it and gain a clear view of the cervix.
- Cell collection: Using a small spatula or brush, the doctor will collect a sample of cells from the cervix. This process is generally painless but may cause mild discomfort for some individuals.
- Speculum removal: Once the sample is collected, the speculum is carefully removed.
- Analysis: The collected cells are then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
How is a Pap test of the anal canal performed?
Here is an overview of the procedure used to perform a Pap test of the anal canal:
- Preparation: Similar to the preparation for a cervical Pap test, it’s advisable to avoid using rectal medications or enemas in the days leading up to the test. Your doctor may provide specific instructions based on individual circumstances.
- Positioning: The individual undergoing the test typically lies on their side with their knees drawn toward their chest. Alternatively, they may be positioned in a bent-over table or in a knee-chest position.
- Digital rectal examination (DRE): Before collecting cells for the Pap smear, your doctor may perform a digital rectal examination. This involves inserting a lubricated, gloved finger into the rectum to feel for any abnormalities, such as lumps or masses.
- Speculum insertion: A small, lubricated speculum may be gently inserted into the anus to provide a clear view of the anal canal.
- Cell collection: Using a brush or swab, your doctor will collect a sample of cells from the anal canal. This process is typically painless but may cause mild discomfort for some individuals.
- Speculum removal: Once the sample is collected, the speculum is carefully removed.
- Analysis: The collected cells are then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
About this article
This article was written by doctors to help you read and understand your pathology report. Contact us if you have any questions about this article or your pathology report. Read this article for a more general introduction to the parts of a typical pathology report.



