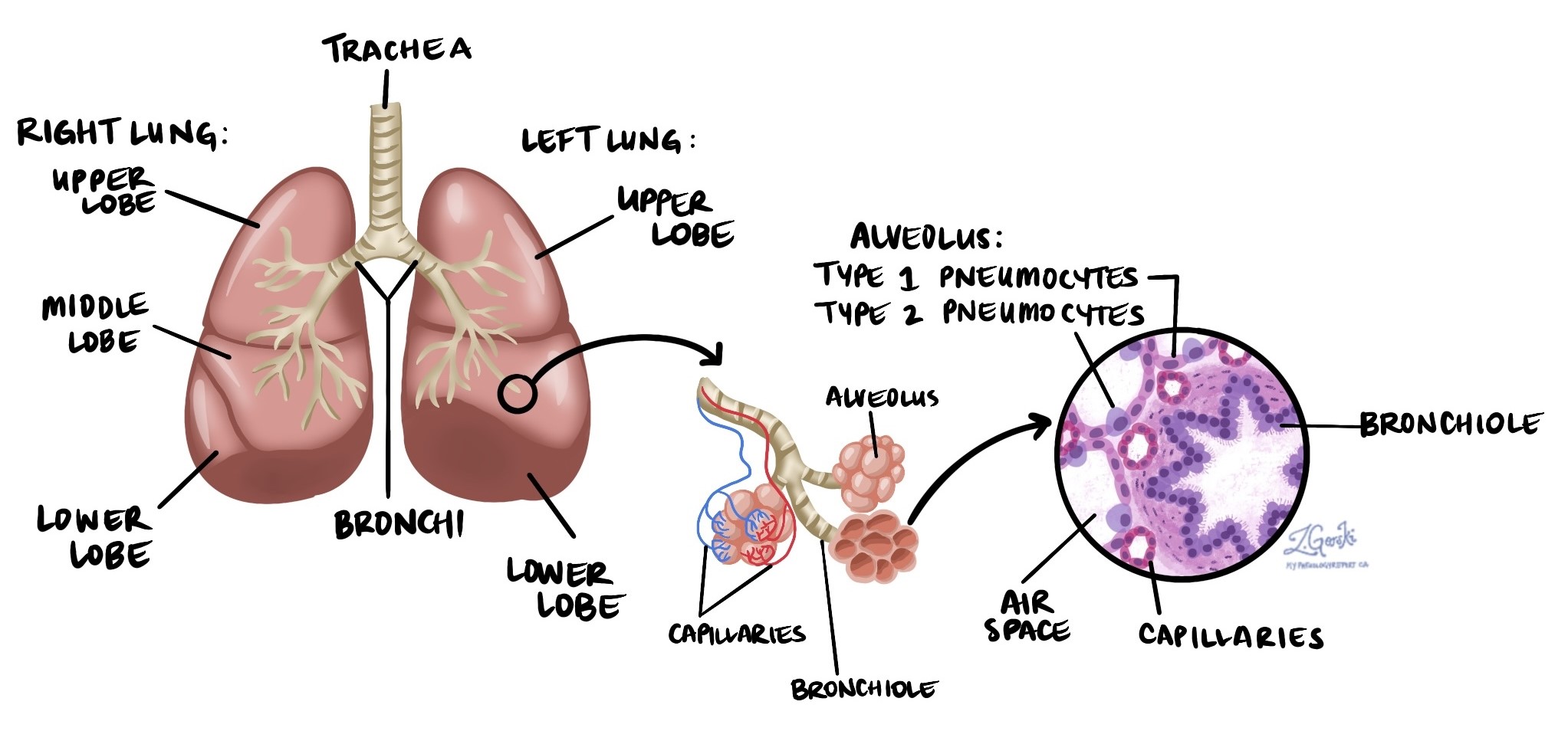
Pneumocytes are specialized cells found in the lungs. They line tiny air sacs called alveoli. Alveoli are important because they help transfer oxygen from the air you breathe into your blood. They also help remove carbon dioxide from your blood so you can breathe it out.
Types of pneumocytes
There are two types of pneumocytes, called type 1 and type 2.
-
Type 1 pneumocytes are very thin cells that cover most of the surface inside each alveolus. Because they are thin, they allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass through easily.
-
Type 2 pneumocytes are rounder, thicker cells that help keep the lungs working properly. They make a substance called surfactant, which helps keep alveoli open, making it easier to breathe. Type 2 pneumocytes also help replace type 1 pneumocytes when the lung is injured.
Why are pneumocytes important in a pathology report?
Pathologists often describe pneumocytes when looking at lung tissue under the microscope. Changes in these cells, such as injury, growth, or unusual shapes, can help diagnose diseases like infections, inflammation, or lung cancer.
Questions to ask your doctor
-
Did my pathology report mention anything unusual about my pneumocytes?
-
Do changes in pneumocytes mean there is damage or disease in my lungs?
-
Will I require any additional tests or treatments based on changes observed in pneumocytes?