By Jason Wasserman MD PhD FRCPC
March 7, 2023
What is chronic cholecystitis?
Chronic cholecystitis is prolonged, or long-standing, inflammation of the gallbladder. It is a very common condition that is more frequently seen in young and middle-aged women.
What does cholelithiasis mean?
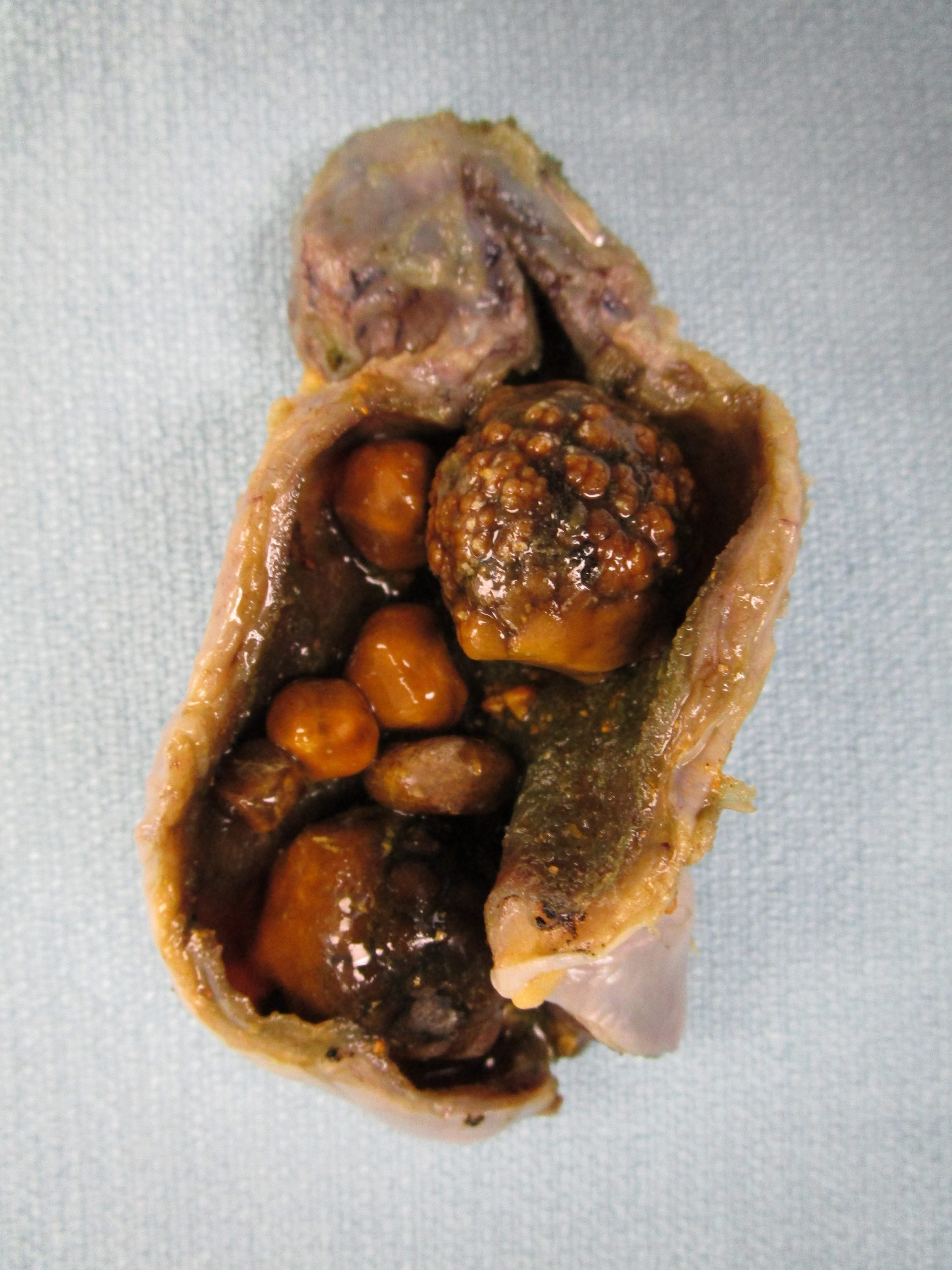
Pathologists use the term cholelithiasis to describe gallstones which are hard, stone-shaped collections of biological material that build up in the gallbladder. Most gallstones are made of cholesterol that comes from the liver. Gallstones can also be made up of bilirubin, which forms when red blood cells break down, or the mineral calcium. Gallstones can cause chronic cholecystitis by filling the gallbladder and preventing it from contracting normally, or by blocking one of the tubes that connect the gallbladder to the small bowel.
What causes chronic cholecystitis?
Chronic cholecystitis is typically caused by gallstones that get stuck in the cystic duct, which is a tube that connects the gallbladder to the small bowel.
What are the symptoms of chronic cholecystitis?
Most people with chronic cholecystitis experience abdominal pain after eating.
How is chronic cholecystitis diagnosed?
The diagnosis of chronic cholecystitis is made after the gallbladder is removed in a procedure called a cholecystectomy. This surgical procedure is usually performed after imaging, such as an ultrasound or CT scan of the gallbladder, shows features that are consistent with chronic cholecystitis.
What does chronic cholecystitis look like under the microscope?
When examined under the microscope, the gallbladder of an individual with chronic cholecystitis shows evidence of prolonged or chronic inflammation. Specifically, a variety of inflammatory cells, including neutrophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and histiocytes, are usually seen in the mucosa on the inside of the gallbladder. Cholesterol is often seen inside the cells that line the gallbladder. Pathologists describe this change as cholesterolosis.
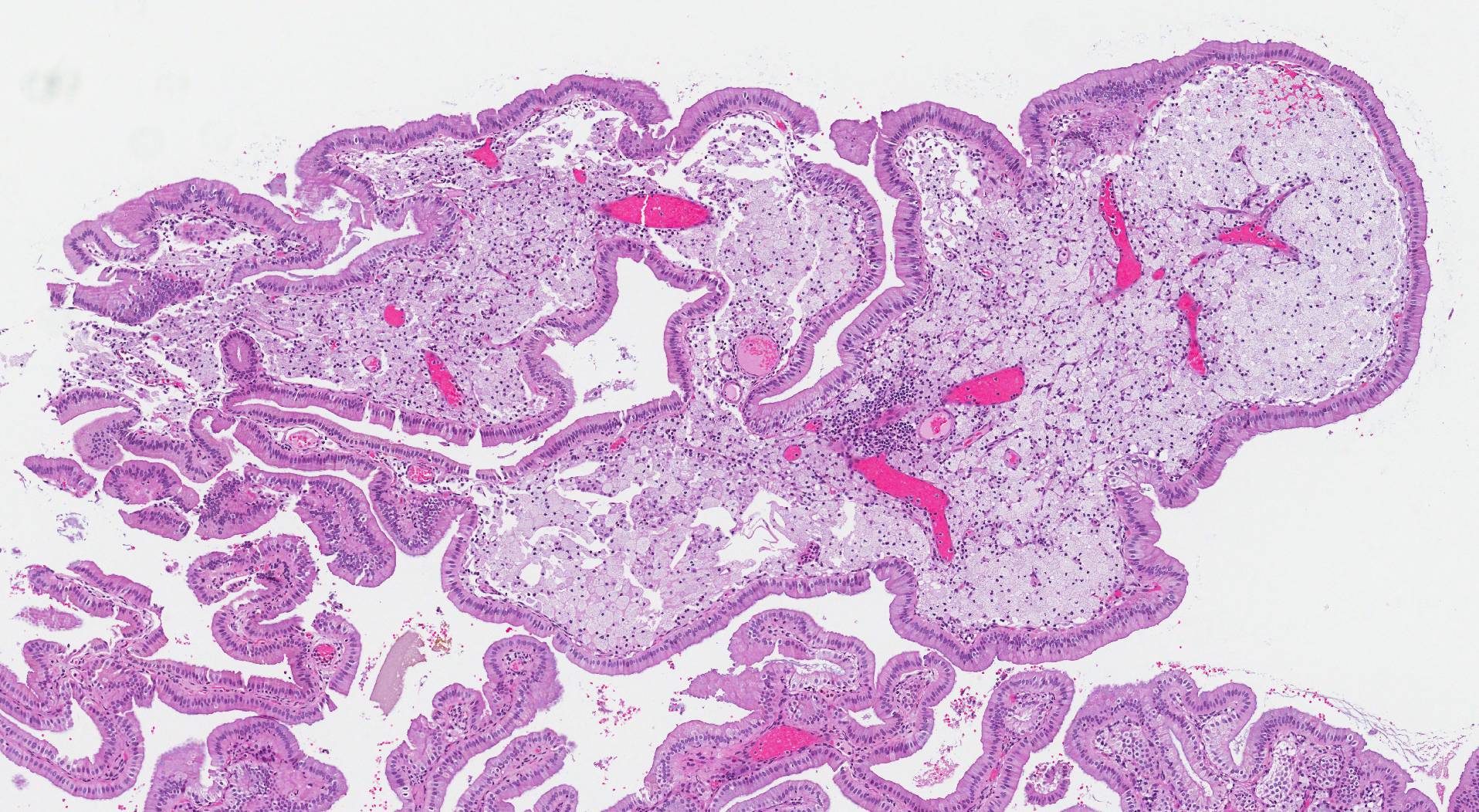
With chronic cholecystitis, the muscular wall of the gallbladder is typically much thicker than normal. Pathologists describe this change as hypertrophy. Hypertrophy occurs because the gallbladder is forced to work harder to get bile past gallstones. In some cases, the epithelium on the inner surface of the gallbladder is pushed deep into the muscular wall. Pathologists describe these areas as Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses.
Finally, adenomyomas are sometimes seen in a gallbladder removed in an individual who has chronic cholecystitis. Adenomyomas (also called adenomatous hyperplasia) are groups of non-cancerous cells, connected together and forming round structures called glands, and surrounded by bundles of muscle cells. They are found within the wall of the gallbladder.



