by Jason Wasserman MD PhD FRCPC
September 13, 2024
A seromucinous hamartoma is a rare, benign growth found in the nasal cavity or the sinuses. The term “hamartoma” refers to a mass made up of an abnormal mixture of cells and tissues that are normally found in the area but have grown in a disorganized way. Seromucinous refers to the combination of serous (watery) and mucinous (mucus-producing) glandular cells that make up the hamartoma. These growths are non-cancerous and typically grow slowly over time.
Is a seromucinous hamartoma benign or malignant?
Seromucinous hamartomas are benign, which means they are not cancerous. Unlike malignant (cancerous) tumours, benign tumours do not invade surrounding tissues or spread to other body parts. However, depending on their size and location, they can still cause symptoms.
What are the symptoms of a seromucinous hamartoma?
Most seromucinous hamartomas do not cause noticeable symptoms and are often found incidentally during imaging or examinations for other reasons. When symptoms are present, they may include nasal congestion, difficulty breathing through the nose, or a sensation of fullness in the nasal cavity. In rare cases, larger hamartomas may cause more significant obstruction or discomfort.
What causes a seromucinous hamartoma?
The exact cause of seromucinous hamartomas is not fully understood. These growths are thought to arise from abnormal development of the glands and tissues in the nasal cavity or sinuses. They are not associated with any known risk factors or environmental exposures, and they do not appear to be inherited.
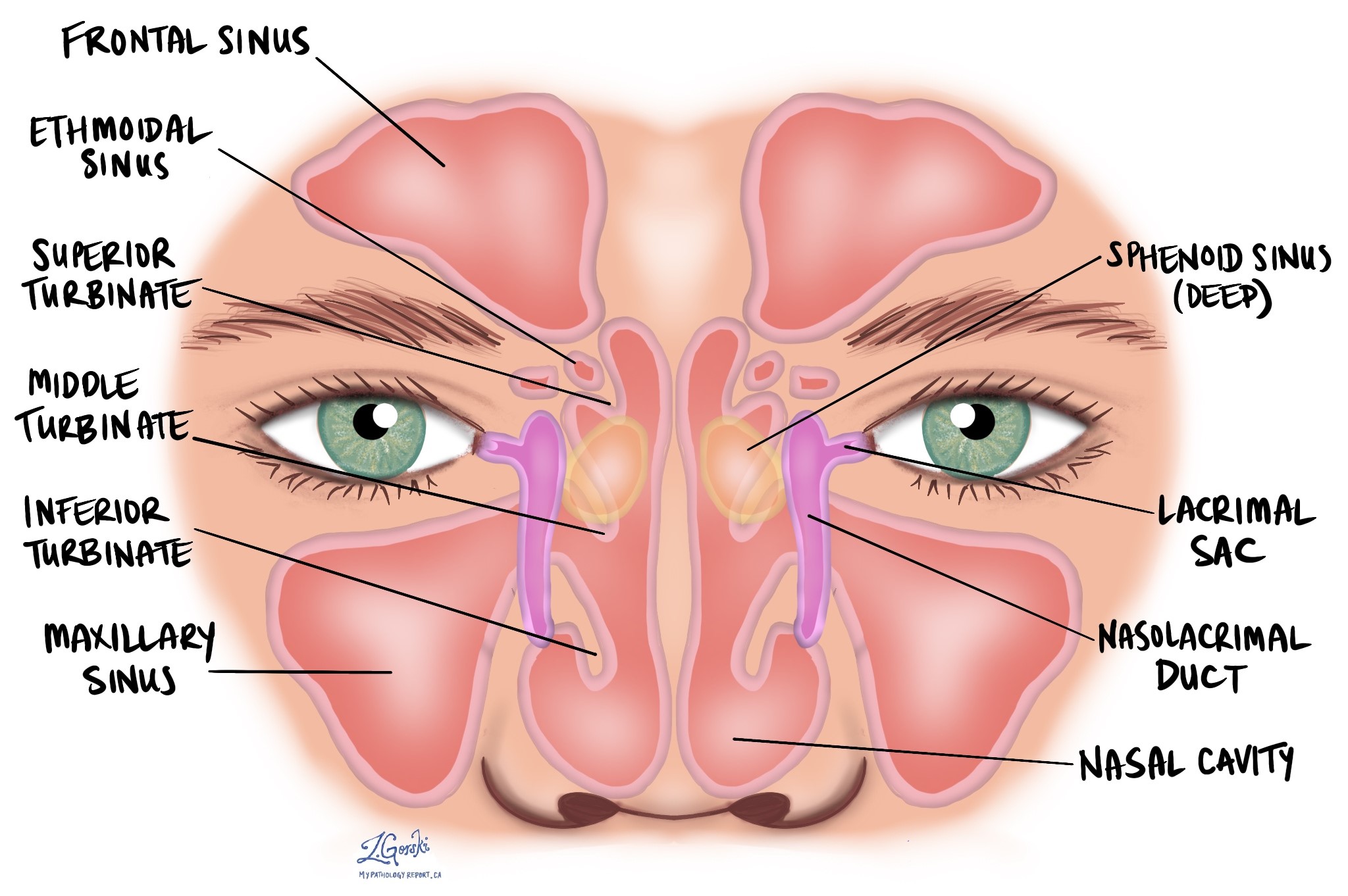
Where are seromucinous hamartomas typically found?
Seromucinous hamartomas are most commonly found in the nasal cavity, particularly in the region of the middle turbinate, a bony structure within the nose that helps regulate airflow. They can also be found in the paranasal sinuses, which are the air-filled spaces surrounding the nasal cavity. These hamartomas are typically small and localized.
What are the microscopic features of a seromucinous hamartoma?
Under the microscope, a seromucinous hamartoma is composed of a mixture of serous (watery) and mucous (mucus-producing) glands. The glands are lined by normal-looking cells, but their arrangement is disorganized, which is typical of hamartomas. The surrounding tissue may show features of fibrosis (scar-like tissue) or mild inflammation, but there are no signs of malignancy, such as invasion of surrounding tissues or abnormal cellular features.



