by Jason Wasserman MD PhD FRCPC
August 10, 2023
What is a thecoma?
A thecoma is an uncommon and noncancerous type of ovarian tumour. The tumour is made up of specialized thecal cells that are normally found in the ovary.
Is a thecoma benign or malignant?
Thecoma is a benign (noncancerous) type of ovarian tumour.
What are the symptoms of a thecoma?
The most common symptoms of a thecoma are related to abnormal hormone production by the tumour. Most tumours produce excess estrogenic hormones. However, symptoms related to excess androgen production are also possible. Large tumours may cause symptoms such as pelvic or abdominal pain and pressure.
What causes a thecoma?
At present, we do not know what causes a thecoma.
How is this diagnosis made?
The diagnosis is made after the entire tumour has been surgically removed and examined under the microscope by a pathologist.
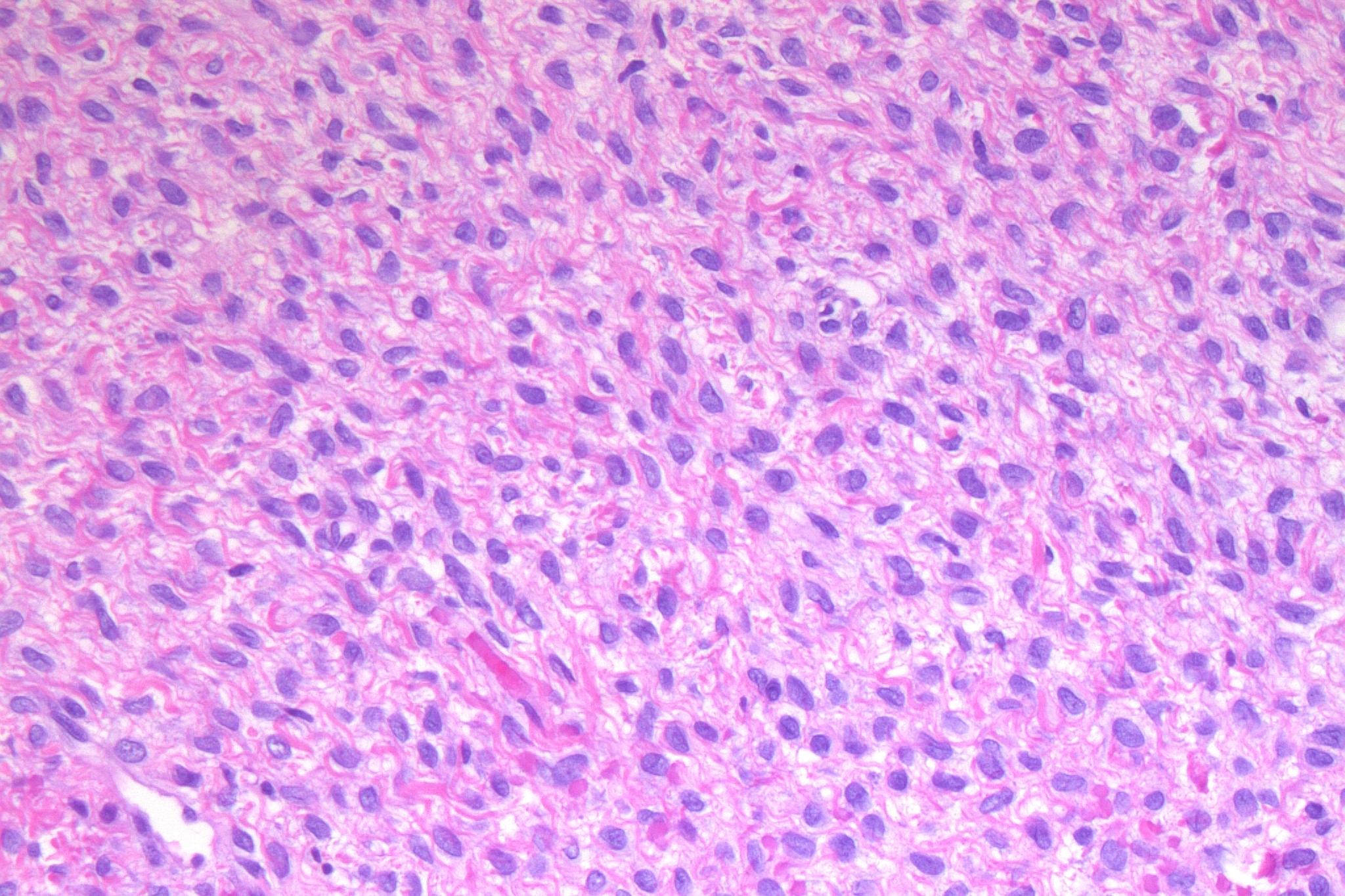
What does a thecoma look like under the microscope?
When examined under the microscope, most thecomas are made up of a uniform population of large tumour cells with pink-grey coloured cytoplasm and round nuclei. These cells resemble the thecal cells normally found in the ovary. Mitotic figures (cells dividing to create new cells) may be seen but should be rare. The tumour cells are typically arranged in nests or large groups called sheets.


