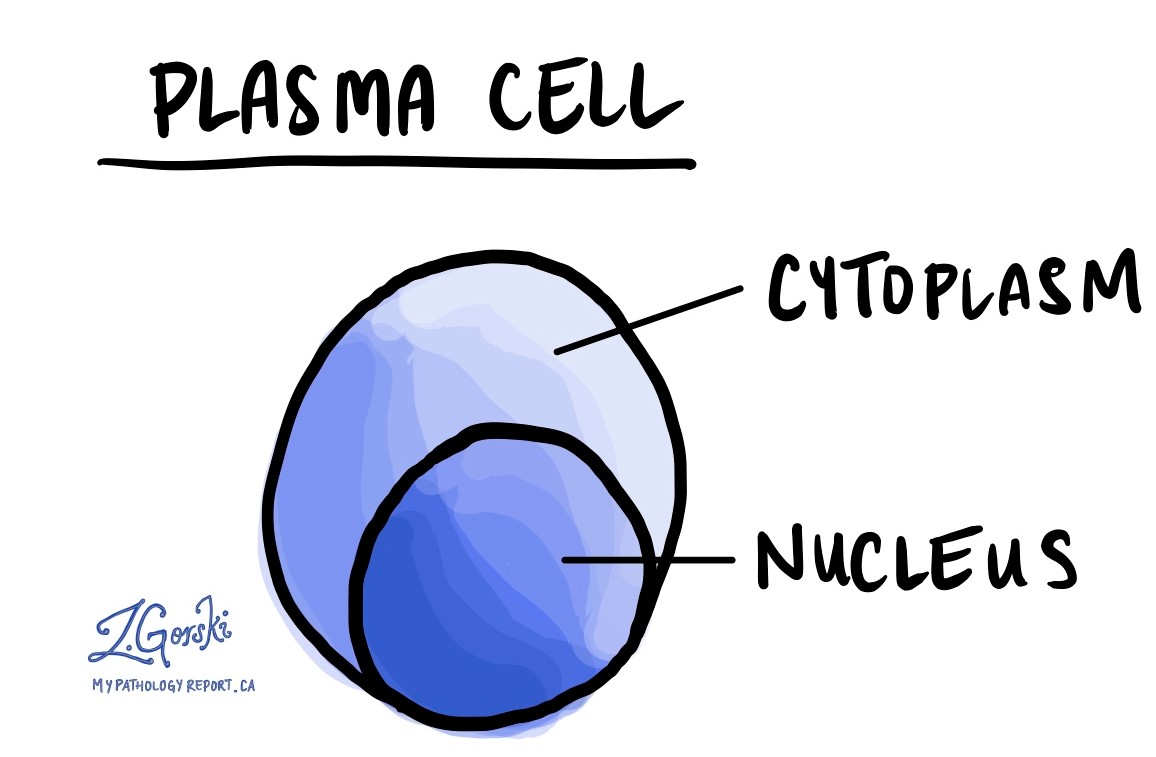
Antibodies also known as immunoglobulins are a special type of protein made by plasma cells. These special proteins protect our bodies by sticking to bacteria and viruses, which makes them easier to remove from the body. They can also stick to abnormal cells or cells that have stopped functioning normally. A plasma cell neoplasm is a type of cancer that makes large amounts of antibodies. The proteins can be found in the blood or urine.
Types of antibodies
Antibodies are made up of four parts and each part is called a chain. One antibody is made up of two heavy chains and two light chains. There are five different kinds of heavy chains, called A, G, D, E, and M, and two different kinds of light chains called kappa and lambda. Any combination of heavy and light chains can be used to make an antibody. These options allow your body to produce many different kinds of antibodies (for example IgA kappa, IgG lambda, etc.). While the immune system can make many different kinds of antibodies, each plasma cell makes just one kind. Because our immune system makes millions of different plasma cells, it is normal to find many different kinds of antibodies in the body at any time.
About this article
Doctors wrote this article to assist you in reading and comprehending your pathology report. Feel free to reach out to us with any questions about this article or your pathology report. To get a comprehensive introduction to your pathology report, read this article.



