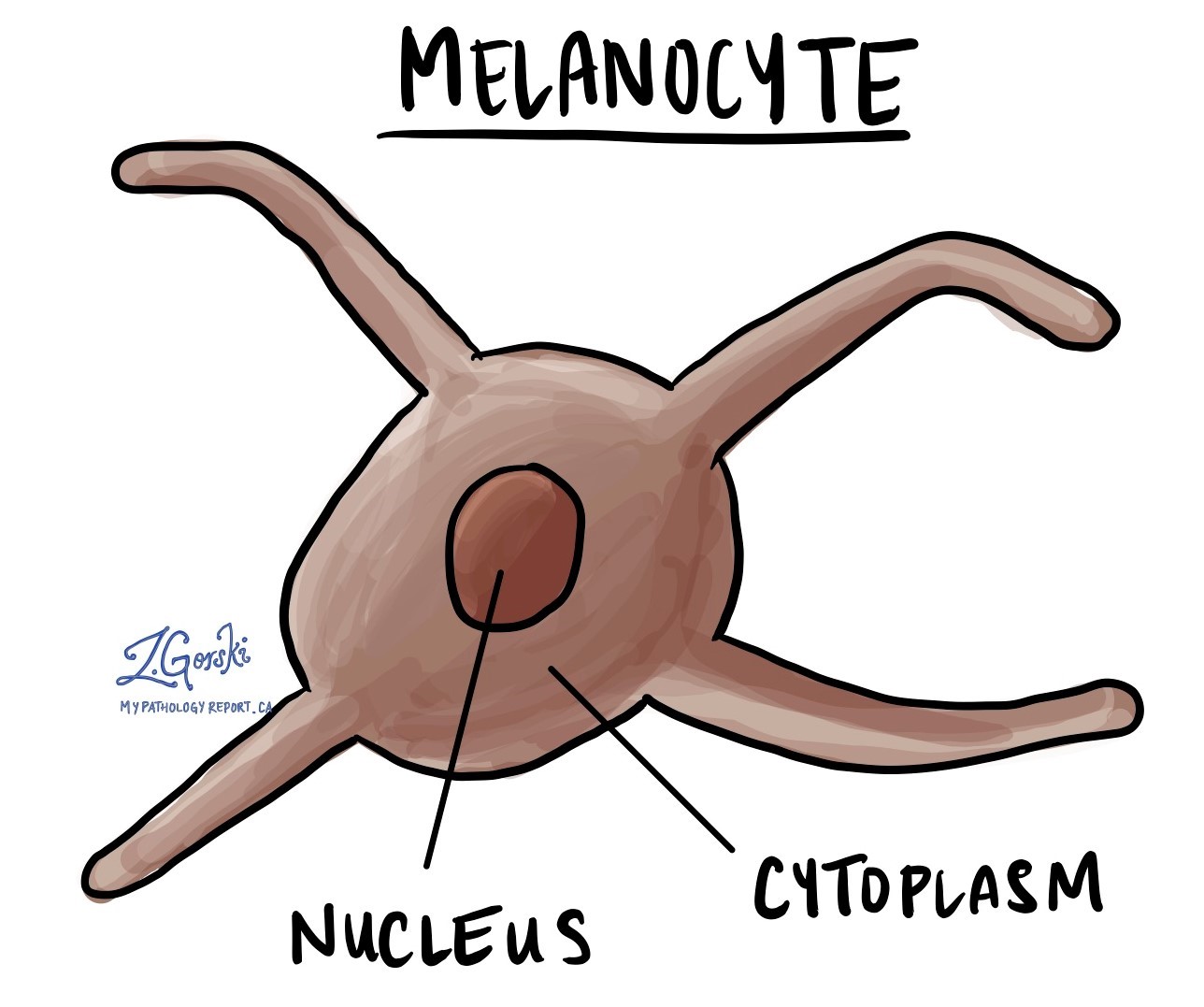
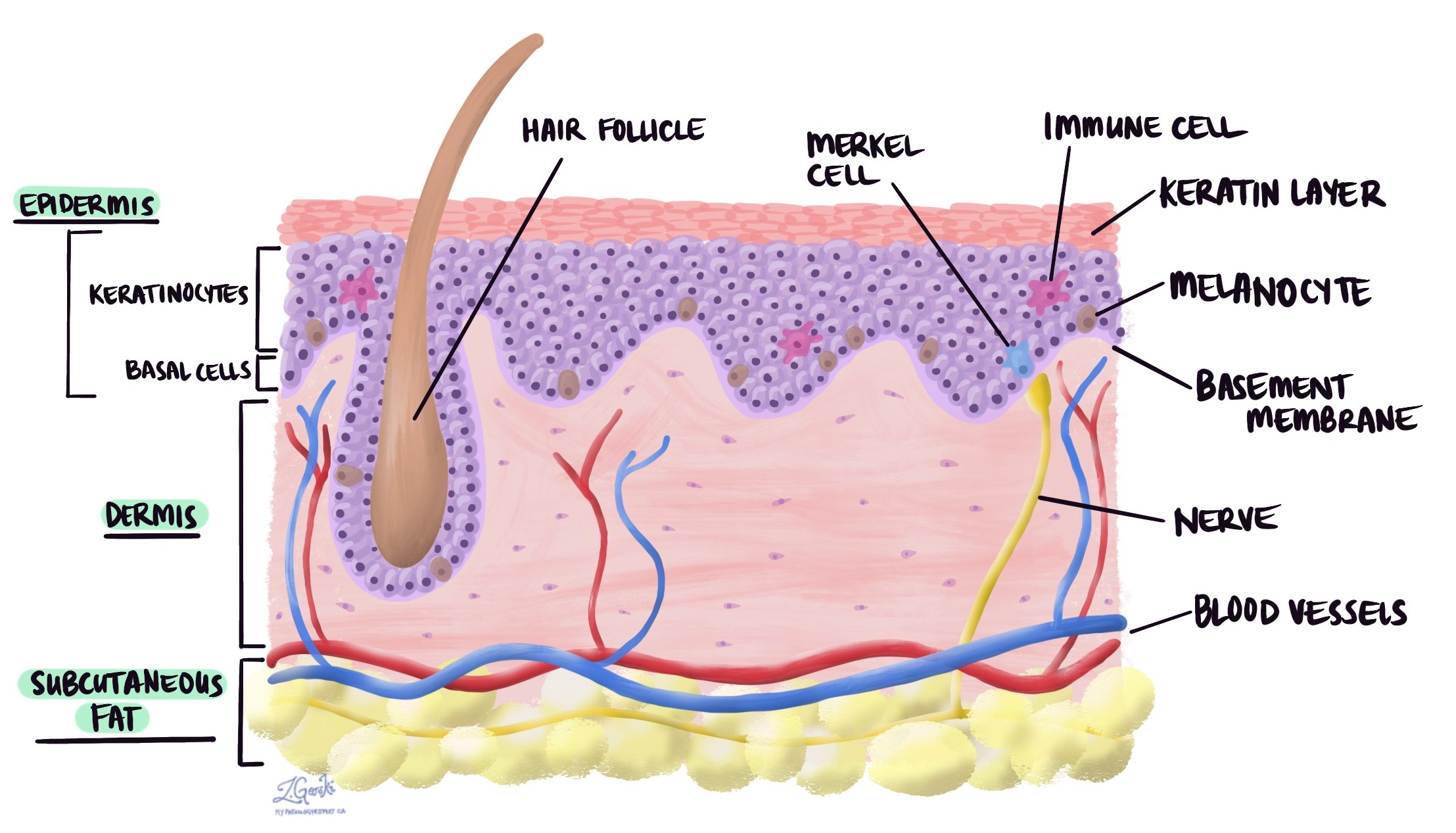
Melanocytes are a type of cell found in the skin and other body parts. These cells produce melanin, the pigment that gives colour to your skin, hair, and eyes. Melanocytes play an important role in protecting your skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
What is their function?
The primary function of melanocytes is to produce melanin, which absorbs UV rays from the sun and helps protect the DNA in your skin cells from damage. When your skin is exposed to sunlight, melanocytes produce more melanin, leading to a darker skin tone or a tan. Melanocytes also help determine your natural skin colour, which is based on the amount and type of melanin they produce.
Where are melanocytes normally found?
Melanocytes are primarily found in the epidermis, the outer layer of the skin, where they are located at the base of the epidermis in an area called the basal layer. They are also found in other parts of the body, including:
- Hair follicles: Melanocytes give colour to your hair.
- Eyes: In the iris, they determine eye colour.
- Ears: They are present in the inner ear.
- Mucous membranes: These include areas like the mouth and nose.
- Leptomeninges: A thin tissue layer covering the brain and spinal cord.
What do melanocytes look like under the microscope?
Under the microscope, melanocytes are small cells with long, branching arms (called dendrites) that extend between neighbouring skin cells. These dendrites allow melanocytes to transfer melanin to other cells, which helps distribute pigment evenly across the skin. In a hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained slide used by pathologists, melanocytes are often seen as cells with clear or lightly pigmented cytoplasm and a darker nucleus. Immunohistochemistry, a technique that highlights specific proteins, is frequently used to identify melanocytes by detecting markers such as S100, HMB-45, and MelanA.
What types of cancer start from melanocytes?
Cancer that starts from melanocytes is called melanoma. Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer and can also develop in other areas where melanocytes are found, such as the eyes (ocular melanoma) or mucous membranes.
Melanoma can begin in an existing nevus (mole) or as a new growth on the skin. If not detected early, it can grow deeper into the skin and spread to other parts of the body. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for improving outcomes.
If you have concerns about melanoma or changes in your skin, your doctor or dermatologist can provide guidance and recommend appropriate steps for monitoring or treatment.