MyPathologyReport
September 24, 2023
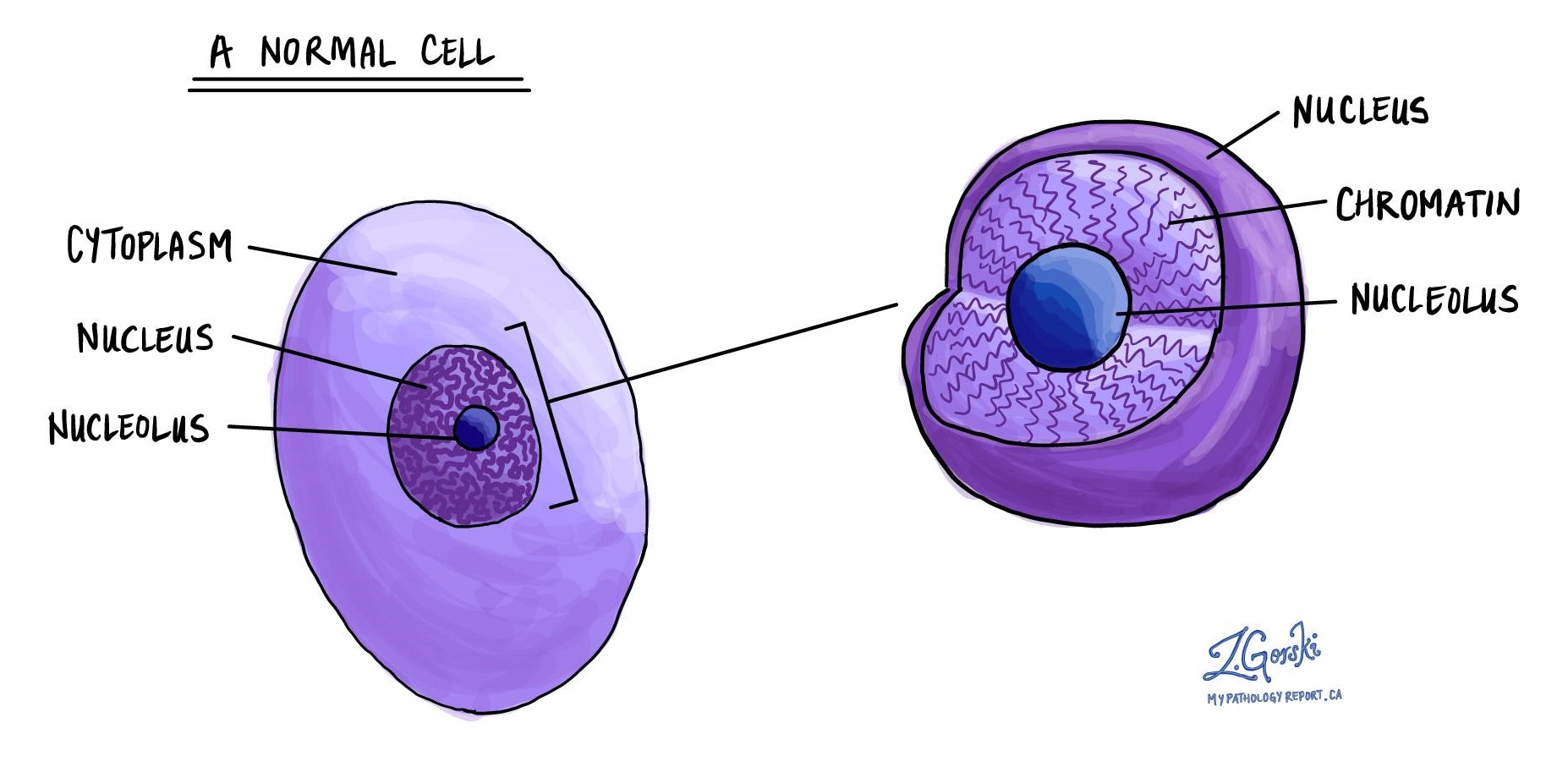
Chromatin in pathology refers to the appearance of the DNA-protein complex within the nucleus of a cell, which can provide valuable insights into the cell’s health, function, and potential abnormalities. The way chromatin is organized and presented can indicate various disease states, including cancer.
- Condensed: This term suggests that the chromatin appears tightly packed or clumped. It’s often associated with cells that are not actively dividing. In a pathological context, highly condensed chromatin can indicate cells undergoing apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cells in a dormant state.
- Dispersed/vesicular: Refers to chromatin that appears loosely organized or distributed throughout the nucleus. This pattern is typically seen in cells that are active in transcription (gene expression) and is common in rapidly dividing cells. In pathology, a vesicular chromatin pattern might indicate a high metabolic or proliferative activity, often seen in tumor cells.
- Margination: This describes the accumulation of chromatin against the nuclear membrane. It can be a sign of cell stress or apoptosis. Margination is sometimes described as chromatin clearing.
- Hyperchromatic: When chromatin appears darker than normal under a microscope, it is described as hyperchromatic. This can indicate a high concentration of DNA, often seen in cancerous cells due to increased DNA content or abnormal chromatin packing.
- Hypochromatic: In contrast, hypochromatic chromatin appears lighter, indicating a lower DNA content. This can be seen in cells with DNA loss or damage.
- Chromatin clumping: This term is used when chromatin aggregates into distinct clumps within the nucleus. It can suggest irregular cell cycles and is often observed in aging cells or cells exposed to toxic agents.
- Fine granular: Describes chromatin that has a finely granulated appearance, indicative of a uniform distribution. This can be a feature of normal cells or certain types of cancer cells, depending on the context and other nuclear features.
The significance of these terms lies in their ability to provide clues about the cell’s state. For example, changes in chromatin organization can signal the presence of cancerous transformations, the response to treatment, or the progression of certain diseases. Pathologists use these observations, along with other histological features, to diagnose and understand the behavior of various diseases at the cellular level.
About this article
This article was written by doctors to help you read and understand your pathology report. Contact us if you have questions about this article or your pathology report. For a complete introduction to your pathology report, read this article.