November 16, 2023
Epithelial cells are specialized cells normally found on the surface of an organ or tissue. They connect to form a thin barrier called an epithelium. Cancers that arise from these cells are called carcinomas.
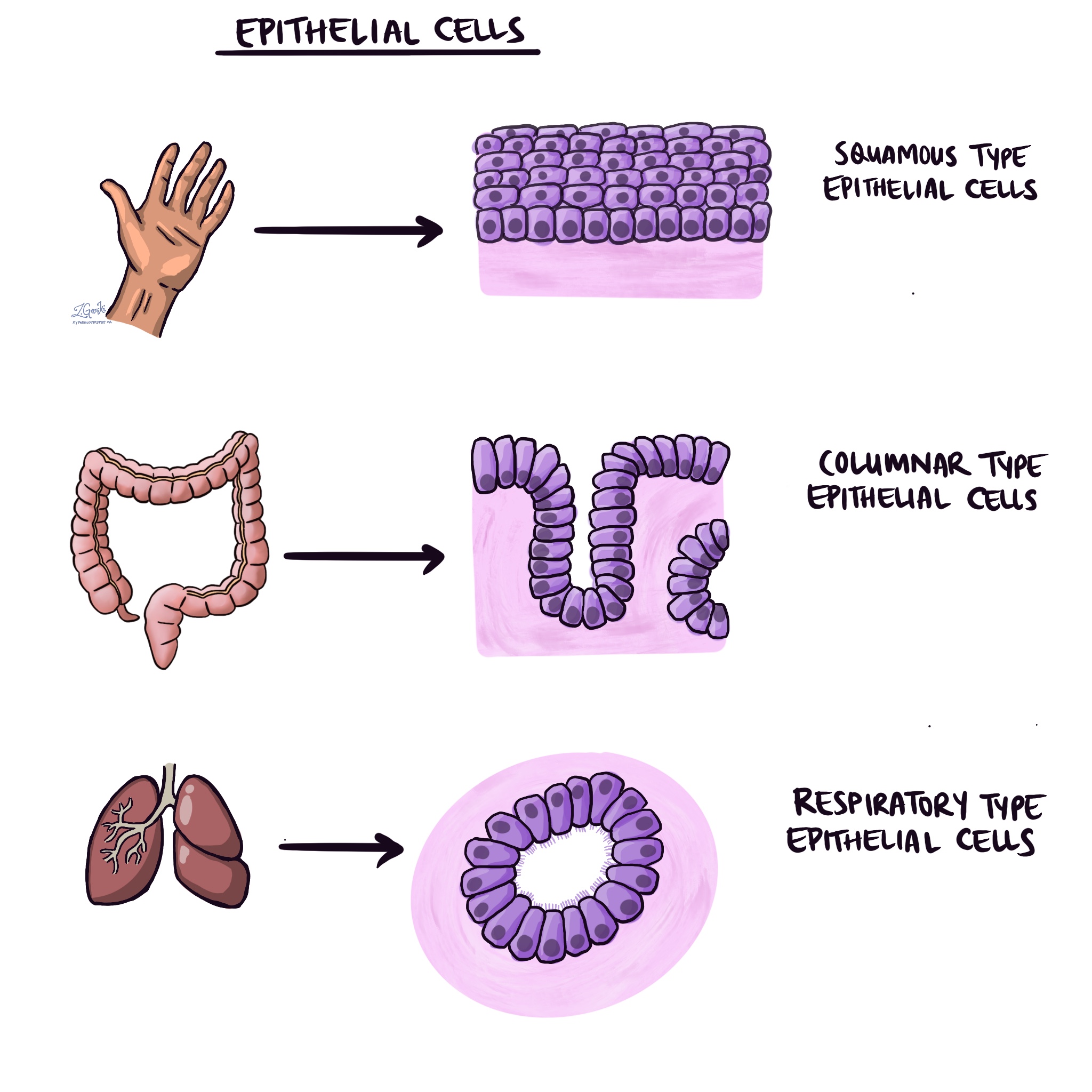
Epithelial cells are divided into different types based on their shape, size, function, and location. Some are flat and thin, some are tall and column-like, and some are cube-shaped. Some are arranged in a single layer, while others are stacked in multiple layers.
What do epithelial cells do?
Some functions of epithelial cells include:
- Protection: These cells form a barrier that keeps out harmful substances, such as bacteria, viruses, dirt, and chemicals, from entering your body or damaging your organs. For example, the squamous-type epithelial cells found on the surface of the skin protect you from infections and injuries.
- Secretion: These cells can produce and release substances, such as hormones, enzymes, mucus, sweat, saliva, and milk, that are needed for your body’s activities or processes. For example, the glandular-type epithelial cells in your sweat glands secrete sweat to help you cool down when you are hot.
- Absorption: These cells can take in substances, such as nutrients, water, oxygen, and drugs, from the environment and transport them to your blood or other cells. For example, the ciliated columnar-type epithelial cells in your small intestine absorb the nutrients from the food you eat and deliver them to your bloodstream.
About this article
Doctors wrote this article to help you read and understand your pathology report. Contact us if you have questions about this article or your pathology report. For a complete introduction to your pathology report, read this article.