T cells, also known as T lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell that plays a vital role in the immune system. These cells are primarily found in lymphoid organs, such as lymph nodes, which are distributed throughout the body. They are also abundant in areas of inflammation caused by infection or injury, where they help coordinate the body’s immune response.
T cells originate from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow. These stem cells are special because they can develop into all the different types of blood and immune cells. Once T cells are formed, they migrate to an organ called the thymus, where they undergo further development and training to distinguish between harmful invaders and the body’s own tissues. After this maturation process, T cells enter the bloodstream and lymphatic system, ready to defend the body against threats.
What is the function of a T cell?
T cells are central to the adaptive immune response, a specialized defense system that provides targeted protection against specific pathogens (such as bacteria and viruses) and abnormal cells. The functions of T cells include:
- Helping other immune cells: Helper T cells (CD4-positive T cells) assist other immune cells, like B cells, in identifying and attacking foreign invaders. They release chemical signals called cytokines, which stimulate the immune response.
- Directly killing infected cells: Cytotoxic T cells (CD8-positive T cells) directly recognize and destroy cells that are infected with viruses or have become cancerous.
- Regulating the immune system: Regulatory T cells help control the immune response, preventing it from attacking the body’s own tissues and reducing inflammation after an infection is cleared.
- Remembering past infections: Memory T cells “remember” specific pathogens the body has encountered before, enabling a faster and stronger immune response if the pathogen is encountered again.
What markers are used to identify T cells?
Pathologists use specific markers to identify T cells and their subtypes. These markers are proteins found on the surface of T cells. The most common markers include:
- CD3: A universal marker for all T cells.
- CD5: Found on most T cells and some other immune cells.
- CD4: Found on helper T cells, which assist other immune cells in fighting infections.
- CD8: Found on cytotoxic T cells, which directly kill infected or abnormal cells.
To detect these markers, pathologists use specialized laboratory techniques such as:
- Immunohistochemistry: A test that uses antibodies to detect specific markers on cells in tissue samples. Results are visible under a microscope.
- Flow cytometry: A method that analyzes cells in a liquid sample to detect the presence of specific markers. This test is especially useful for identifying T cell subtypes and their functions.
Common types of T cell cancer
Cancers that develop from T cells are called T cell lymphomas. These are rare cancers that affect the lymph nodes, skin, blood, or other organs. Below are some of the most common types of T cell cancer.
Peripheral T cell lymphoma (PTCL)
Peripheral T cell lymphoma is a diverse group of aggressive cancers that develop in mature T cells. Patients often experience symptoms such as swollen lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Treatment typically involves chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or stem cell transplantation.
Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL)
Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma, a subtype of PTCL, commonly affects older adults and is associated with immune dysfunction. It can cause enlarged lymph nodes, rash, fever, and anemia. Depending on the stage and severity of the disease, treatment options include chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
Cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL)
Cutaneous T cell lymphoma is a type of lymphoma that primarily affects the skin, with subtypes such as mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome. These tumours often present as red, scaly patches or plaques that may itch or become painful. Treatment may include skin-directed therapies, radiation, or systemic treatments for advanced stages.
T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (T-ALL/T-LBL)
T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma is a cancer of immature T cells that can manifest in the blood as leukemia or in the lymph nodes as lymphoma. Symptoms often include fatigue, frequent infections, easy bruising, and swollen lymph nodes. Treatment usually involves intensive chemotherapy and, in some cases, stem cell transplantation.
Adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL)
Adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma is a rare and aggressive cancer associated with infection by the human T cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1). Patients may present with skin lesions, swollen lymph nodes, and an increased risk of infection. Treatment typically involves chemotherapy or antiviral therapies tailored to the specific subtype of ATLL.
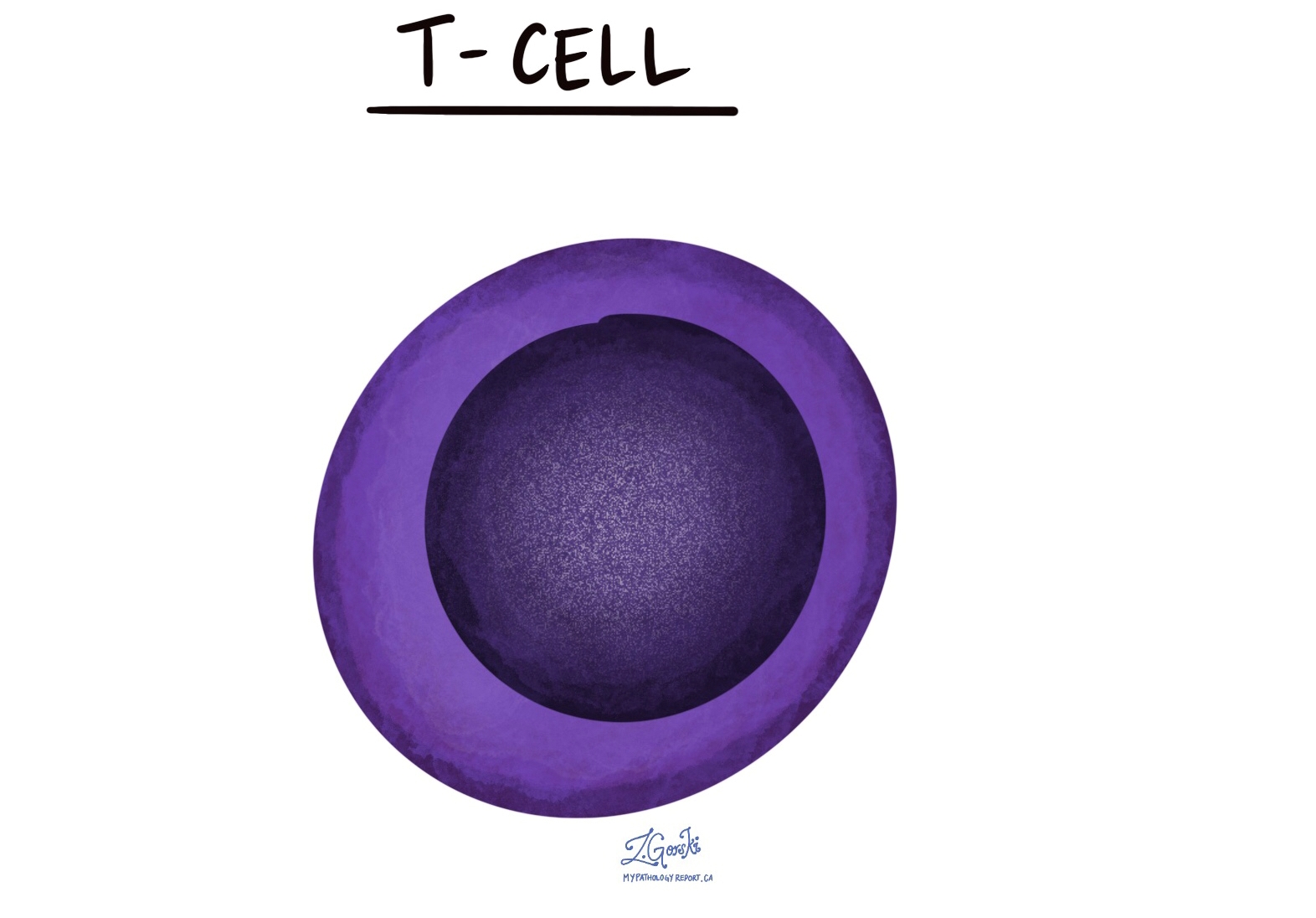
What do T cells look like under the microscope?
Under the microscope, T cells are small, round cells with a large, dark nucleus and a thin rim of light-colored cytoplasm. The nucleus often takes up most of the cell, giving T cells a dense appearance. In tissue sections, T cells may be seen scattered throughout lymphoid organs, such as the lymph nodes and spleen, or clustered in areas of inflammation.
About this article
Doctors wrote this article to help you read and understand your pathology report. Contact us if you have questions about this article or your pathology report.



