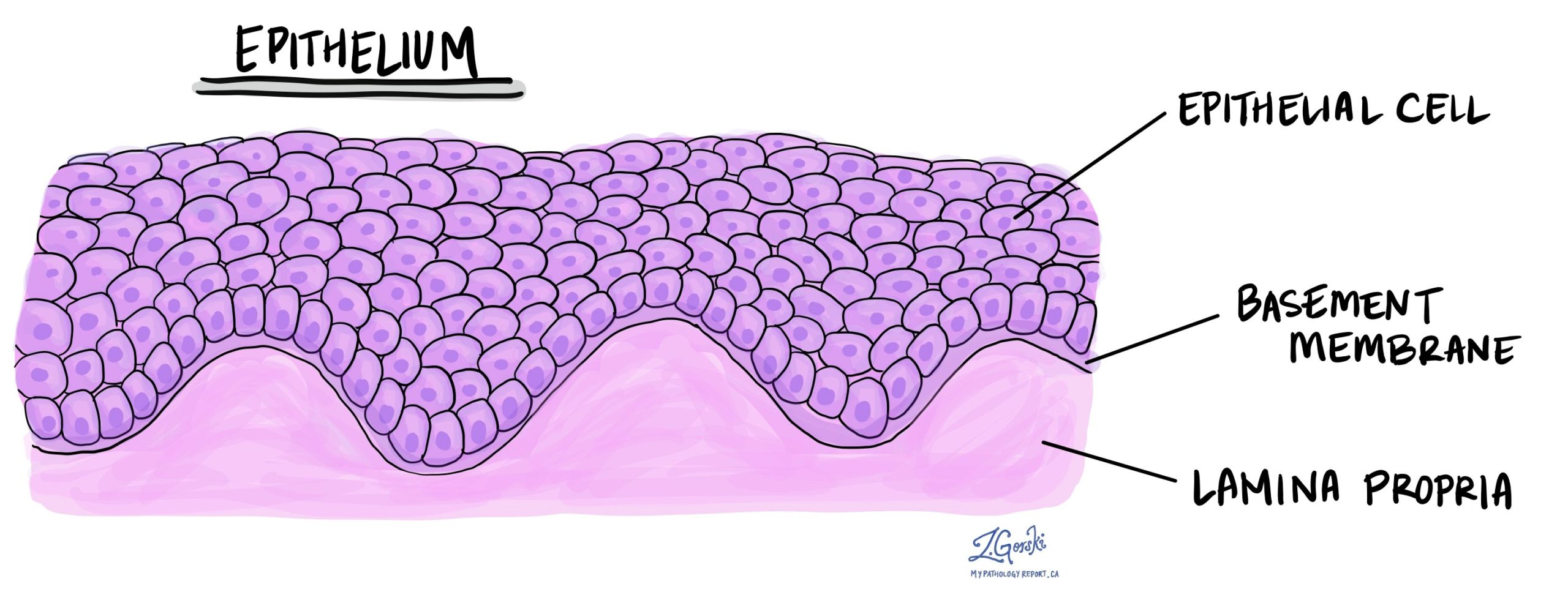
The epithelium is a type of tissue composed of one or more layers of cells that cover the body’s surfaces, line internal cavities and organs, and form glands. This tissue serves several key functions including protection, absorption, filtration, excretion, secretion, and sensory reception. Epithelial cells are tightly packed, with minimal intercellular space, and are attached to a thin layer of connective tissue known as the basement membrane, which supports and separates them from underlying tissues.
Where is this type of tissue normally found?
Epithelial tissue is found throughout the body, both covering external surfaces and lining internal spaces and structures. Some examples include:
- Skin: Forms the outer covering of the body, protecting against dehydration, injury, and infections. The surface is made up of specialized squamous cells.
- Digestive tract: Lines the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, and rectum, facilitating absorption and secretion.
- Respiratory system: Lines the nasal passages, trachea, and lungs, involving infiltration and moisture retention. This type of tissue is referred to as respiratory-type epithelium.
- Urinary system: Lines the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, involved in filtration and excretion. This type of tissue is referred to as the urothelium.
- Reproductive tracts: Lines structures in both the male and female reproductive systems, involved in various reproductive functions.
- Glands: Both endocrine (releasing hormones directly into the blood or lymph) and exocrine (releasing substances through ducts to an epithelial surface) glands are derived from epithelial tissue.
What kind of cancers start from the cells in the epithelium?
Cancers that originate from epithelial cells are known as carcinomas, and they are the most common type of cancer. Types of carcinomas include:
- Squamous cell carcinoma: Arises from squamous epithelium found in places like the skin, mouth, esophagus, and the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts.
- Adenocarcinoma: Originates from glandular epithelial cells that line or cover organs such as the breast, prostate, lung, stomach, pancreas, and colon.
- Basal cell carcinoma: The most common type of skin cancer, arising from the basal cells in the epidermis.
- Urothelial carcinoma: Starts in the urothelium, which lines the urinary bladder, ureters, and parts of the kidneys and urethra.
- Renal cell carcinoma: Arises from the epithelial cells of the renal tubules in the kidney.
The identification and classification of carcinomas is important for determining the most effective treatment strategies, as different types of epithelial cancers can vary significantly in their behavior, spread, and response to treatments.
About this article
Doctors wrote this article to help you read and understand your pathology report. Contact us if you have questions about this article or your pathology report. For a complete introduction to your pathology report, read this article.